Py5Shape.specular()#
Sets the specular color of a Py5Shape object’s material, which sets the color of highlight.
Examples#
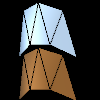
def create_strip(r, g, b):
s = py5.create_shape()
s.begin_shape(py5.TRIANGLE_STRIP)
s.fill(0, 51, 102)
s.specular(r, g, b)
s.vertex(10, 40, -25)
s.vertex(20, 0, -10)
s.vertex(30, 40, 0)
s.vertex(40, 0, 5)
s.vertex(50, 40, 0)
s.vertex(60, 0, -10)
s.vertex(70, 40, -25)
s.end_shape()
return s
def setup():
py5.size(100, 100, py5.P3D)
py5.background(0)
py5.light_specular(255, 255, 255)
py5.directional_light(204, 204, 204, 0, 0, -1)
py5.shape(create_strip(255, 255, 255), 0, 5)
py5.shape(create_strip(204, 102, 0), 0, 50)
Description#
Sets the specular color of a Py5Shape object’s material, which sets the color of highlight. Specular refers to light which bounces off a surface in a preferred direction (rather than bouncing in all directions like a diffuse light). Use in combination with Py5Shape.emissive(), Py5Shape.ambient(), and Py5Shape.shininess() to set the material properties of a Py5Shape object.
This method can only be used within a Py5Shape.begin_shape() and Py5Shape.end_shape() pair. The specular color setting will be applied to vertices added after the call to this method.
This method has additional color functionality that is not reflected in the method’s signatures. For example, you can pass the name of a color (e.g. “green”, “mediumpurple”, etc). Look at the online “All About Colors” Python Ecosystem Integration tutorial for more information.
Underlying Processing method: PShape.specular
Signatures#
specular(
gray: float, # value between black and white, by default 0 to 255
/,
) -> None
specular(
rgb: int, # color to set
/,
) -> None
specular(
x: float, # red or hue value (depending on current color mode)
y: float, # green or saturation value (depending on current color mode)
z: float, # blue or brightness value (depending on current color mode)
/,
) -> None
Updated on December 25, 2023 16:36:33pm UTC